MARKETING GLOSSARY
Everything you always wanted to know about marketing but were afraid to ask!
“API (application program interface) is a set of routines, protocols, and tools for building software applications. Basically, an API specifies how software components should interact. Additionally, APIs are used when programming graphical user interface (GUI) components”. Learn more about API Development
Source: Webopedia
Attribution reporting shows you each interaction a donor or customer had with your organization, from their first visit to your website, through to becoming a donor or customer. It allows you to attribute different amounts of credit to different points on the journey, from how you got the lead/contact, to what they did just before donating. (See also Closed-Loop Reporting.)
The buyer’s journey is the active research process a buyer (or patient, supporter, client, etc.) goes through leading up to a purchase (or an appointment, donation, etc.)
As illustrated in the book Marketing 4.0 by Philip Kotler, the buyer’s journey in the age of connectivity is reflected as the Five A’s: aware, appeal, ask, act and advocate.
In inbound marketing, we often also refer to the buyer’s journey in three stages: awareness, consideration, and decision.
Yodelpop Source: Marketing Collateral Checklist
Campaign management is the planning, execution, tracking, and analysis of a marketing initiative; sometimes centered around a new product launch or an event. Campaigns normally involve multiple pushes to potential buyers through email, social media, surveys, print materials, giveaways, etc. all focusing on a similar topic or idea.
Source: Wrike
Closed-loop reporting shows you each interaction a donor or customer had with your organization, from their first visit to your website, through to becoming a donor or customer. (See also Attribution Reporting.)
A competitive advantage is a set of exclusive features of a company and/or its products, which offer a company a superior position within the market. It is one of the primary factors contributing to brand loyalty. Examples of a competitive advantage would be low cost, higher quality or better support.
Conscious Capitalism is a movement that seeks an approach to businesses that is based on a higher purpose that serves and aligns the interest of all stakeholders and harnesses the power of business and capitalism to create value for all people and the environment.
Source: Conscious Capitalism: Liberating the Heroic Spirit of Business
Contact management is a strategy that focuses on using a software program (like HubSpot) to easily store and source a contact’s information, including their name, contact history, email information, and more. Inbound marketing is all about attracting your contacts with helpful information, and a strong contact management strategy provides you with the tools to deliver contextual content to your contacts.
Source: HubSpot
Inbound marketing content is material that is created for a given target audience. In relation to inbound marketing, content is a piece of information that exists for the purpose of being digested (not literally), engaged with, and shared. Content typically comes in the form of a blog, video, social media post, photo, slideshow, or podcast, although there are plenty of over types out there. From website traffic to lead conversion to customer marketing, content plays an indispensable role in a successful inbound marketing strategy. Learn more about content marketing.
Source: HubSpot
Content creation is the development of information to any media and most especially to digital media for an end‑user/audience in specific contexts. Typical forms of content creation include maintaining and updating web sites, blogging, photography, videography, online commentary, the maintenance of social media accounts, and editing and distribution of digital media.
Source: Wikipedia
A widely cited definition of content marketing (published both by HubSpot and the Content Marketing Institute) is:
A strategic marketing and business process focused on creating and distributing valuable, relevant, and consistent content to attract and retain a clearly defined audience, and ultimately, to drive profitable customer action.
Content marketing comes in many formats such as blogs, pillar pages, ebooks, videos, webinars, white papers, case studies, and infographics.
Yodelpop Source: The Ultimate Guide to Nonprofit Content Marketing
Conversion path is the sequence of touchpoints a user engages in before converting on a given point of conversion. Touchpoints are different interactions, across different channels that typically include compelling content, a call‑to‑action, a landing page, a confirmation or thank you page, and sometimes a follow‑up email(s).
Marketers build out and optimize these conversion paths to continually improve the conversion rate.
The number of people who complete a form on a landing page divided by the total number of people who visited the page.
Source: Wrike
The customer‑perceived value concept can, therefore, be used to identify how to better compete in the market. This requires assessing product/service benefits and costs and comparing them to competitor product/service benefits and costs. While this sounds simple, the comparison is complicated by the fact that there are many types of perceived benefits (product, services, personnel, image) and many types of perceived costs (monetary, time, energy, psychological). It is further complicated by the fact that customers are not always rational decision-makers and/or have complete control over their purchase decisions (more on this later).
A competitive advantage is a set of exclusive features of a company and/or its products, which offer a company a superior position within the market. It is one of the primary factors contributing to brand loyalty. Examples of a competitive advantage would be low cost, higher quality or better support.
Database management is basically the housekeeping of managing contacts by keeping a database updated to make sure the most accurate and usable information is available, and that efforts to segmentation and personalization are not impeded by unreliable data.
Source: HubSpot
Differentiation is what your organization does to make a product or service more desirable to a target/niche market, thereby gaining an advantage over your competitors. When you engage in differentiation, you add specialized aspects (but aspects that have broad appeal) to your existing products or services. When you engage in differentiation focus, you develop a product or service that in and of itself appeals to a niche market.
Digital marketing is the promotion of brands, products or services through channels using digital devices such as computers, phones, and tablets. It includes content marketing, search engine marketing (SEM), email marketing, social media marketing, short message service (SMS), display advertising, and any other marketing via digital media. When compared with analog marketing, digital marketing requires not only different tools but a deeper understanding of consumer behavior.
Digital economy refers to an economy that is based on digital computing technologies, although we increasingly perceive this as conducting business through markets based on the internet and the World Wide Web. The digital economy is also sometimes called the Internet Economy, New Economy, or Web Economy.
Source: Wikipedia
Email marketing is the use of email to promote products and/or services, typically to a group of people. But a better email marketing definition is the use of email to develop relationships with potential customers and/or clients by providing valuable, educational and highly relevant content.
The place your page visitors will supply information in exchange for your offer. It’s also how those visitors can convert into precious sales leads. As a best practice, only ask for information you need from your leads in order to effectively follow up with and/or qualify them.
Source: HubSpot
Green marketing refers to marketing a product or service focused on the environmental benefits of the product or service. Green marketing can involve a number of different things, such as creating an eco‑friendly product, using eco‑friendly packaging, adopting sustainable business practices, or focusing marketing efforts on messages that communicate a product’s green benefits.
Source: Shopify
Greenwash references superficial or insincere display of concern for the environment shown by an organization through their messaging. Greenwash happens when a brand makes sustainability claims in their marketing messaging that they can't or don’t back up in operations.
Yodelpop Source: Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Marketing
Growth driven design is an approach to web development where a launch‑pad site is developed and published quickly, updated constantly, and dynamic. Rather than requiring a long up‑front build time, a growth‑driven design process gets a basic site up and running then proceeds to make incremental changes ongoing using real‑time data and process of prioritizing development items based on their perceived impact on return on investment.
Growth‑driven design is an innovative way of creating a website that shortens the time to launch, is driven by results and increases ROI.
Yodelpop Source: Traditional & Growth‑Driven Web Design
A growth stack is a set of software applications and platforms that work together to connect marketing, sales, and service. It is a cohesive set of sales and marketing technology that allows organizations to connect their activities seamlessly with the connective tissue that enables human‑centered, efficient marketing.
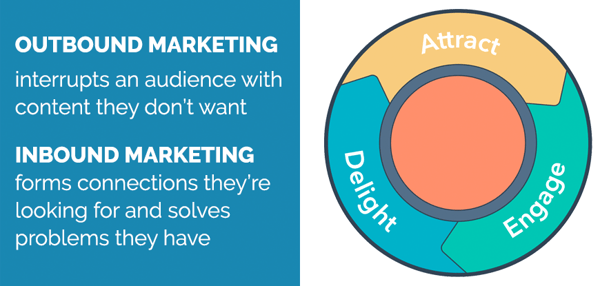
Inbound marketing is a business methodology that attracts customers by creating valuable content and experiences tailored to them. While outbound marketing interrupts an audience with content they don’t want, inbound marketing forms connections they’re looking for and solves problems they already have. By creating content designed to address the problems and needs of your ideal customers, you attract qualified prospects and build trust and credibility for your business. Learn more about Inbound Marketing.
Source: What Is Inbound Marketing, HubSpot
Influencers can have multiple meanings when it comes to marketing. An influencer can be a thought leader—someone who influences general thought on a topic.
In the sales and marketing process, an influencer can be someone who may work alongside an ideal prospect who is more of the final decision‑maker when it comes to buying.
A key message or brand platform is a source document that gives a company or organization a concise, strategic, and consistent way of describing its work, value, and target audience. As a document, it is strictly internal and not publicly shared. However, the language in it is designed to be copied and pasted into all branding, strategy and marketing materials. It typically includes mission, vision, history, core style principles, elevator speech, and other pieces of information that do not change frequently. Learn more about Brand Platforms.
A keyword strategy is the strategy for using keywords in your online content to attract visitors. It involves selecting high‑performing keywords that drive relevant traffic to your business. A keyword strategy is needed both to attract organic traffic and to plan successful search engine advertising. The best keyword strategies rely on highly relevant keywords, which are keywords that relate closely to your business or are associated with your industry.
Source: WordStream
A person who goes from being an anonymous website visitor to a being a known contact to your business or organization, with you having their email address and possibly other information about them. This process occurs as the visitor provides his or her contact information in exchange for valuable content.
Lead generation is the process of attracting new leads. It is a marketing tactic that drives a person to demonstrate an interest in a product or service. Online this traditionally happens by providing valuable content in exchange for contact information from a website visitor. Learn more about lead generation.
Sometimes referred to as “drip marketing,” lead nurturing is the practice of developing a series of communications (emails, social media messages, etc.) that seek to qualify a lead, keep it engaged, and gradually push it down the sales funnel. Inbound marketing is all about delivering valuable content to the right audience—and lead nurturing helps foster this by providing contextually relevant information to a lead during different stages of the buying lifecycle.
Source: HubSpot
Lead scoring is a methodology used to rank prospects against a scale that represents the perceived value each lead represents to the organization. The resulting score is used to determine which leads a receiving function (e.g. sales, partners, teleprospecting) will engage, in order of priority.
Source: HubSpot
The American Marketing Association’s definition of marketing is:
Marketing is the activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large.
Marketing is a function alongside operations and finance; marketing creates demand for an organization's product or service.
Yodelpop Source: Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Marketing
Marketing automation refers to software platforms designed for organizations and marketing teams to more effectively market on multiple channels online (such as email, social media, websites, etc.) and automate repetitive tasks.
Originally focused on email marketing automation, marketing automation refers to a broad range of automation and analytic tools for marketing. Marketing Automation platforms typically a third party web‑based solution, such as HubSpot or Constant Contact.
Source: Wikipedia
The marketing function at a company or organization is a core function of an organization, alongside finance, operations, accounting, and research and development. Marketing is often perceived as a creative profession and is sometimes therefore misidentified non‑essential. However, the marketing function creates the demand for products and services, without which other core functions would not exist.
Source: Principles of Marketing Management, Kotler & Keller
The marketing mix is a tool to help plan what to offer and how to offer to the target market, or what the firm can do to engage consumers and offer value. Traditionally, this is broken down into the 4 P’s: product, price, (what to offer) place and promotion (how to offer).
In the digital economy, the marketing mix concept has evolved to accommodate more customer co‑creation: The 4 C’s include co‑creation (customization and personalization), currency (flexible pricing, price fluctuations based on demand), communal activation (instant access to products and services) and conversation (social proof).
Source: Principles of Marketing Management, Kotler & Keller & Marketing 4.0, Philip Kotler
“Marketing organization is the interface of the firm with its markets and where the work of marketing gets done.” It includes “four elements of marketing organization—capabilities, configuration (including structure, metrics, and incentives), culture, and the human capital of marketing leadership and talent.” These are mobilized through marketing activities (the seven As) that enable a company to “(1) anticipate market changes, (2) adapt the strategy to stay ahead of the competition, (3) align the organization to the strategy and market, (4) activate effective implementation, ensure (5) accountability for results, (6) attract resources, and (7) manage marketing assets.”
Source: Abstract, Journal of Marketing: Moorman & Day, “Organizing for Marketing Excellence,” 2016.
A marketing strategy is a plan of marketing strategies that will help the organization achieve its overall strategic goals. An ideal marketing strategy would include a detailed plan for each business, product or brand. Marketing plans typically include the following sections: an executive summary, current marketing situation, threats and opportunities analysis, objectives, marketing strategy, action plans, and budget.
Source: Principles of Marketing Management, Kotler & Keller & Marketing 4.0, Philip Kotler
A marketing workflow delivers emails to contacts in response to actions they take, with the goal of nurturing a relationship and gaining their business when they are ready. Components include:
- Enrollment criteria: What triggers the first email (e.g., persona, content downloaded, etc.)
- Emails: Series of emails solving the contact’s challenges
- Delays: Period of time to wait between emails
- If/then branching logic: Actions to take based on different criteria met by the contact
- Goal: When the contact meets this goal (e.g., becomes a customer), they leave the workflow
A mission statement articulates the core of what an organization (whether a business or a nonprofit) does and an aspirational outcome that it is pursuing. It is a statement that is short in length, but long on vision. The organization’s mission statement is the number one marketing asset, and a well-crafted marketing strategy starts with an understanding of the mission.
Yodelpop Source: How to Write A Mission Statement
MQL is an acronym for “marketing qualified lead.” An MQL is defined as a more deeply engaged, sales-ready contact than usual leads, but who have not yet become fully fledged opportunities for sales. It’s important for a marketing team to have an agreed-upon definition (based on data) of what attributes determine what a marketing qualified lead toward the marketing goals.
Off-page or off-site SEO refers to actions taken outside of your own website to impact your rankings within search engine results pages. Optimizing for off-site ranking factors involves improving search engine and user perception of a site's popularity, relevance, trustworthiness, and authority. This is accomplished by other reputable places on the Internet (pages, sites, people, etc.) linking to or promoting your website, and effectively vouching for the quality of your content.
Source: Moz
The practice of integrating multiple channels to create a seamless and consistent customer experience; this involves taking steps to integrate multiple online and offline channels to drive customers to the commitment to make a purchase.
Source: Marketing 4.0, Philip Kotler
On-page SEO (search engine optimization) is the process of enhancing and fine‑tuning your web page content and HTML source code to improve ranking on search engine results pages and increase organic traffic. While the Google search algorithm is constantly being revised and updated, factors that contribute to the on‑page SEO include the page’s, title, URL, image alt‑tags and headings.
A pillar page is a comprehensive resource page that covers a core topic in depth and links to high‑quality content created for the supporting subtopics. This page should apply consistent on‑page SEO best practices, referencing the core topic in the page title, URL, and H1 tag. Ideally, a pillar page sits on the top level of your website in a space that already gets a lot of organic traffic.
Content on a pillar page should also be adapted to convert visitors to leads or leads to customers since this is the canonical piece of information you’re pushing visitors to. Your pillar page will gain authority with a number of quality inbound links from your subtopic content. To ensure that everything on the page can be crawled by SEO engines and discovered by potential customers, the pillar page should not have any content locked behind a form or a password.
Want to see how other users are building their pillar pages? You can check out a few examples on the HubSpot Marketing blog here.

A positioning statement is a sentence that describes what a company or organization does better than anyone else, in relation to their customers or those they wish to serve. It differentiates the company or organization’s products and/or service from its competitors. It can be created using a positioning statement template, such as:
“We [WHAT: provide this service/value/outcome] for [WHO: this type of company/industry/market] by [HOW: using this kind of approach] because [WHY].”
Yodelpop Source: Marketing Collateral Checklist
Premium content refers to content that is longer, more in‑depth, and likely more difficult to digest than your average blog post. This type of content is usually best for downloading and reading over a longer period of time, or for having available to refer back to throughout the research process.
Good examples of this include:
- Ebooks
- Whitepapers
- Case Studies
- Spec Sheets
- Product guides
- Comparison Guides
- Research papers
- Webinars
- Checklists
- Larger Infographics
Source: Waypost
Process automation refers to the use of digital technology to perform a process or processes in order to accomplish a workflow or function. The term “business process automation” is also used to describe digital process automation.
Source: Tallyfy
Relationship marketing is “attracting, maintaining, and enhancing customer relationships,” as defined by Leonard Berry in 1983. It seeks to build a relationship with all customers (unlike frequency marketing). It focuses on building and maintaining a long-term relationship that leads to sales (unlike direct marketing. And it identifies the needs of individual customers and builds them into a base of customers (unlike database marketing). Inbound marketing takes the foundation of relationship marketing and uses internet technology to fully actualize it.
Source: Glenn Voss and Zannie Voss
Responsive design is an approach to web design that makes web pages render well on a variety of devices and window or screen sizes.
Source: Wikipedia
Return on marketing investment is a measure of the performance of marketing to assess the net return from a marketing investment divided by the costs of the marketing investment. It measures the profits generated by investments in marketing activities.
ROMI can be hard to measure. While we typically think of measuring return on investment in dollars, marketing returns such as engagement, advertising, and brand-building impact aren't easily translated into dollars.
Source: Principles of Marketing Management, Kotler & Keller & Marketing 4.0, Philip Kotler
Smart or dynamic content is content that can change based on the interests or past behavior of the viewer or contact, allowing marketers to offer a more targeted and personalized experience to website visitors or contacts. Different messages targeted to different audience segments can be set up within the same email or within a single website page.
Source: HubSpot

S.M.A.R.T. is an acronym for this goal‑setting strategy. It stands for "specific," "measurable," "attainable," "relevant," and "time‑bound." Incorporating these characteristics allows goals to become concrete targets with measurable results.
- Specific. There's a hard and fast metric to reach
- Measurable. The goal's progress can be tracked and quantified
- Attainable. Ensure that the goal is rooted in reality
- Relevant. Related to the company's overall business goals
- Time‑bound. keeps you on schedule
S.M.A.R.T. goals make it easier to set goals, create buy‑in, alignment and a clear direction for your marketing or sales efforts.
Yodelpop Source: Setting Goals for Your Marketing Plan
A smart list, also known as an active list, is a list of contacts that meet a set of criteria, as indicated in their contact records. Contacts are added to or removed automatically based on whether those criteria are met. For example, a smart list could be used to gather all leads. When a lead becomes a customer, a property value in the contact’s record changes. As a result, they are removed from the leads list.
A social enterprise is an organization that uses a business approach to maximize outcomes in financial, social and environmental well‑being—this may include maximizing social impact alongside profits for external shareholders.
Social enterprises can be structured as a for‑profit or non‑profit, as well as one of other types of companies such as B Corps.
Social enterprises have both business goals and social goals. As a result, their social goals are embedded in their objective, which differentiates them from other organizations and corporations.
Source: Wikipedia
Subtopics are shorter pieces of content that answer a specific question about the core topic covered on your pillar page. When you add a new subtopic, you'll be able to view analytics in the Subtopic validation section to determine if your subtopic is a good fit. In addition to Domain Authority, Monthly Search Volume, and Relevancy, you will also see Core Topic Similarity, which measures how closely your subtopic relates back to the core topic on a scale of 0‑100%.
You can attach the following types of content to your subtopics:
- One of your HubSpot blog posts
- The full URL of a webpage
- A link to high-quality external resources
When you attach a webpage, landing page, or blog post to a new subtopic, your topic cluster will keep track of how many inbound links you have referring back to your pillar page to ensure you're setting yourself up for success.
Yodelpop Source: Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Marketing
Sustainability marketing is an outward practice that helps bring about a society in which striving for sustainability is the norm. Products or services can be marketed in a way that encourages society to be more environmentally aware and responsible. Sustainability marketing focuses on promoting the benefits of being a conscious consumer.
Yodelpop Source: Ultimate Guide to Sustainable MarketingSystems integration relevant to marketing refers to the integration of various tools that are used for marketing and sales where integration makes it possible for the tools to talk to each other, or share information.
For example, an association platform may use an integration with the marketing automation platform to sync information about contacts. More widely used integrations may be available via third‑party software. Often times custom integrations are created using custom API, or an application program interface.
Traditional web development involves a classic ‘one and done project model where the entire site is built in a 3‑6 month timeline where the full scope of the website is built from the ground up all at once and remains static until the next redesign.
Yodelpop Source: Traditional & Growth Driven Web Design
Technical SEO (or traditional SEO) is a discipline of setting baseline technical elements in place on a webpage to help the process of ranking well in organic search. Technical SEO is not the same as content SEO, which focuses more on the topic-rich content while technical SEO focuses on the meta tags, such as description and title, in addition to many other ‘behind the scenes’ elements of a given webpage.
Topic clusters are a collection of interlinked articles or pages around one umbrella topic or pillar page. They ultimately allow you to provide greater visibility for search engines to identify your content.
Within this subject, you’ll have a wide range of more detailed, hyper‑focused pages that relate back to the main pillar page. All of these pages linking back tell the search engines that your pillar page is an authority on the topic and that they should pay attention to it.
Source: Impact
A primary sustainability strategy is the triple bottom line. Developed by entrepreneur John Elkington, this approach is about finding opportunities to build competitive advantage across three areas of an organization: financial, environmental and social impacts. This approach broadens the consideration of stakeholders beyond shareholders to all groups that are impacted by the organization.
Yodelpop Source: Ultimate Guide to Sustainable Marketing
User‑generated content is defined as any type of content that has been created and published by unpaid contributors or, using a better term, fans. It can refer to pictures, videos, testimonials, tweets, blog posts, and everything in between and is the act of users promoting a brand rather than the brand itself.
Source: Tint
ABOUT YODELPOP
Yodelpop is a nonprofit marketing agency, creating inbound marketing and optimal user experiences aligned with sustainable goals.

